Quantifying the Optical Depth of Mixed-Phase Clouds Accurately with Passive Observations
Submitter
Turner, David D. — NOAA Global Systems Laboratory
Area of research
Cloud Distributions/Characterizations
Journal Reference
Turner, DD, and EW Eloranta. 2008. "Validating mixed-phase cloud optical depth rerieved from infrared observations with high spectral resolution lidar." IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensinsing Letters 5: 285-288, doi:10.1109/LGRS.2008.915940.
Science
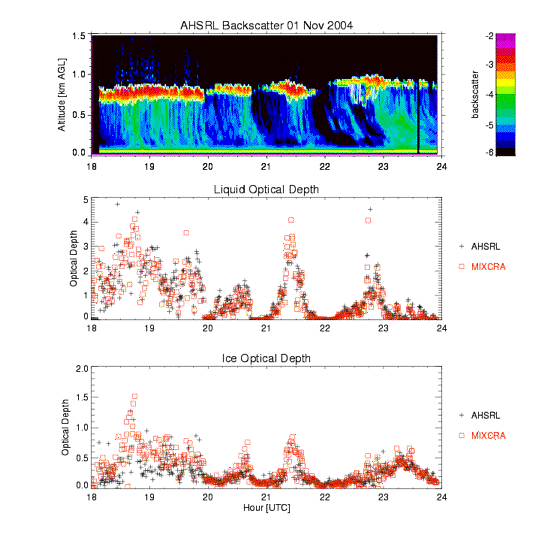
Mixed-phase clouds, or clouds that contain both water droplets and ice particles in the same contiguous cloud, are difficult to characterize quantitatively with remote sensors. The lack of accurate cloud property data for these clouds hinders the ability of the scientific community to model these clouds, their interactions with the surrounding environment, and their lifetimes. Mixed-phase clouds occur frequently over the ARM Climate Research Facility (ACRF) site at Barrow, Alaska, and thus the ARM data collected at this site may help understand these cloud types. In particular, the data from the Atmospheric Emitted Radiance Interferometer (AERI) can be used to retrieve properties of mixed-phase clouds. The AERI-ba
Impact
In the autumn of 2004, the ARM Program conducted the Mixed-Phase Arctic Cloud Experiment (M-PACE) at Barrow and over northern Alaska. One of the ob
Summary
This validation of the AERI-ba